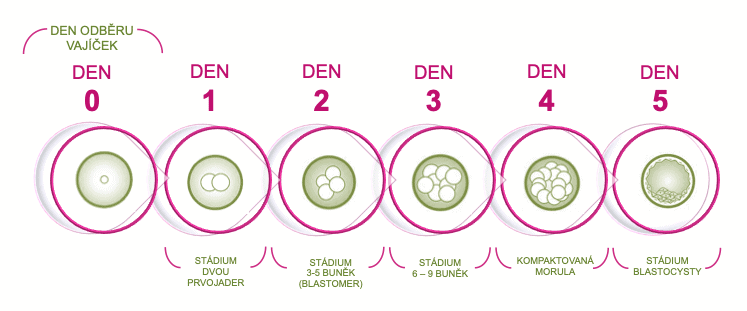
EXTENDED CULTIVATION MEANS THAT THE EMBRYO IS CULTIVATED LONGER IN EMBRYOLOGY LABORATORY AND THE TRANSFER TO THE UTERUS OCCURS ONLY FIVE DAYS AFTER FERTILIZATION.
At this time, the embryo is already in the blastocyst stage, which is a stage that only one third of the embryos reach on average. Thus, the method of extended cultivation is considered as a method of selecting the best quality embryos.
Within the normal IVF cycle, about three-day-old embryos are transferred to the uterus, depending on their development. In the case of natural fertilization of the egg, the three-day-old embryo is located in the fallopian tube and descends to the uterus only on the fifth or sixth day after fertilization.
We recommend a five-day cultivation of embryos when there are a sufficient number of embryos produced as this enables us to select the healthiest embryos for transfer. When only a few embryos are produced, (2-3) and they show differences in development, it may be possible to transfer the embryos into the uterus on the second or third day of cultivation.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF EXTENDED CULTIVATION?
- transfer on the fifth day enables more favorable conditions for embryo implantation and penetration into the endometrium
- this procedure increases the chances of successful treatment by 10-15%.
- cells removed from the surface of the blastocyst on the fifth day after fertilization are suitable for genetic testing
- blastocysts (5-day-old embryos) can be frozen by vitrification and thus preserved with a good prognosis of development after their thawing for future cycles
